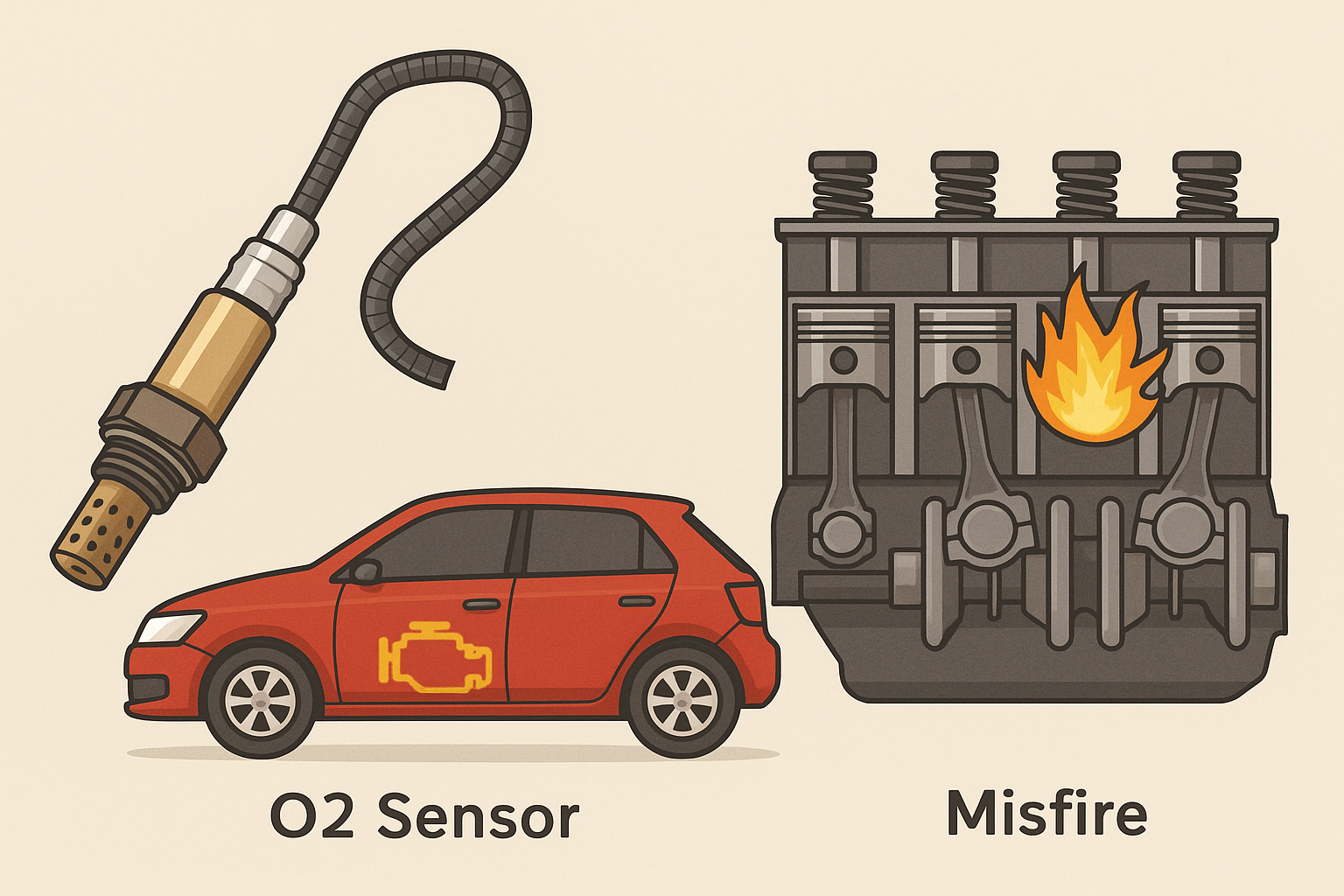
You’re driving along when suddenly the check engine light comes on. The engine starts to feel rough, and maybe you even notice it sputtering. A quick scan at the mechanic shop reveals a faulty oxygen sensor. But can such a small part really be responsible for something as serious as a misfire?
In this article, we’ll explain how O2 sensors work, how they can cause misfires, and what you can do to fix the issue before it leads to more expensive damage.
Can an O2 Sensor Cause a Misfire?
Yes, an O2 sensor can cause a misfire—typically in an indirect way. When an oxygen sensor fails, it may send inaccurate readings to the engine control unit (ECU). This throws off the air-fuel mixture, potentially resulting in inefficient combustion. Over time, this imbalance can lead to engine misfires.
Although it’s a small component, the oxygen sensor plays a crucial role in engine performance and fuel management. If it goes bad, the ripple effect can be significant.
What Is an O2 Sensor and What Does It Do?
The oxygen sensor, or O2 sensor, is a key part of your car’s emission control system. It’s located in the exhaust stream and measures the level of oxygen in the gases leaving the engine. This data helps the ECU fine-tune the air-fuel ratio for optimal performance.
There are usually two types of O2 sensors:
- Upstream (before the catalytic converter)
- Downstream (after the catalytic converter)
The upstream sensor has the greatest impact on engine operation. When it fails, your engine may run too rich or too lean—both of which can trigger misfires.
What Is an Engine Misfire?
An engine misfire occurs when a cylinder fails to complete the combustion cycle correctly. It may be due to a spark plug not firing, insufficient fuel, or poor timing. This disrupts engine balance and can lead to noticeable performance issues.
Typical symptoms of a misfire include:
- Jerky acceleration
- Rough idling
- Engine vibration
- Check engine light
- Increased fuel consumption
Ignoring misfires can lead to serious problems like catalytic converter damage or engine wear.
How a Bad O2 Sensor Can Cause a Misfire
When an O2 sensor sends incorrect information, it alters the air-fuel ratio in the combustion chamber. Here’s how that leads to misfires:
- Incorrect air-fuel mix: The engine may run too lean or too rich.
- Poor combustion: This results in incomplete burning of fuel.
- Secondary damage: Spark plugs can foul due to excess fuel or unburned deposits.
A faulty upstream O2 sensor is more likely to cause these problems since it influences real-time engine performance.
Other Symptoms of a Failing O2 Sensor
A bad oxygen sensor usually doesn’t fail silently. Here are some signs to look for:
- Check Engine Light: Triggered by related codes (e.g., P0130–P0167).
- Lower fuel efficiency: A failing sensor may cause the engine to consume more fuel.
- Failed emissions test: Your vehicle may exceed pollution limits.
- Rotten egg smell: Often caused by catalytic converter stress.
- Hesitation or stalling: Inconsistent fuel delivery can lead to performance hiccups.
How to Diagnose a Faulty O2 Sensor
Detecting a bad O2 sensor requires some diagnostic tools and basic inspection:
- OBD-II scanner: Check for codes such as P0133, P0171, or P0172.
- Live data readout: A good sensor will show fluctuating voltage; a faulty one may appear stuck.
- Visual inspection: Look for wiring damage, buildup, or corrosion.
- Fuel trim analysis: Abnormal readings in fuel trim data may point to sensor failure.
If you’re not confident in reading the data, a certified technician can assist.
Fixing a Misfire Caused by a Bad O2 Sensor
Once you’ve identified the oxygen sensor as the root cause, follow these steps to fix the misfire:
- Replace the faulty sensor: Use a reliable OEM or high-quality aftermarket part.
- Clear error codes: Reset the ECU using an OBD-II scanner.
- Conduct a test drive: Ensure that the issue is resolved.
- Inspect related components: Check for wear or damage on spark plugs, coils, and injectors.
Addressing the issue quickly can restore normal performance and prevent further damage.
How to Prevent O2 Sensor Failure and Misfires
Preventive care goes a long way in maintaining sensor health and engine performance:
- Use quality fuel and engine oil
- Keep your gas tank above a quarter full
- Change air filters regularly
- Address oil or coolant leaks promptly
- Replace sensors every 60,000–100,000 miles (check your manual for specifics)
Staying proactive can reduce the chances of unexpected engine trouble.
Other Possible Causes of Engine Misfire
O2 sensors aren’t the only reason engines misfire. If replacing one doesn’t solve the problem, consider these alternatives:
- Worn-out spark plugs or wires
- Faulty ignition coils
- Clogged or leaking fuel injectors
- Vacuum leaks
- Malfunctioning mass airflow (MAF) sensor
A full inspection may be necessary to identify the correct issue.
Conclusion
So, can an O2 sensor cause a misfire? Absolutely. Though small, this component plays a major role in fuel regulation and combustion. When it fails, the resulting air-fuel imbalance can easily cause misfiring and other drivability issues.
If you’re experiencing poor performance, unusual vibrations, or a check engine light, don’t ignore the signs. Replacing a bad O2 sensor might be the simple fix your engine needs to run smoothly again.
FAQs
Will a bad O2 sensor always cause a misfire?
Not always, but it can trigger conditions—like improper air-fuel mixture—that lead to misfires.
Can I drive with a bad O2 sensor?
Yes, but prolonged driving can damage your catalytic converter and worsen misfire issues.
How much does it cost to replace an O2 sensor?
Typically between $100 and $300, depending on your vehicle and labor rates.
How long do O2 sensors last?
Usually between 60,000 and 100,000 miles, depending on your driving conditions.
Can I replace an O2 sensor myself?
Yes, if you have basic tools and access to the sensor. If not, a mechanic can do it quickly and safely.